Ultrasonic Magnetic Vortex Flow Meter Manufacturer, Sure We Are, Sure To Be Better | ✉ overseas@suremeter.com
Ultrasonic Magnetic Vortex Flow Meter Manufacturer, Sure We Are, Sure To Be Better | ✉ overseas@suremeter.com
Heating is an essential aspect of modern life, providing warmth and comfort to homes and businesses during the cold seasons. The process of heating, particularly in the thermal power industry, is governed by four fundamental elements that work in harmony to deliver heat efficiently.
· Heat Source: The Heart of Heating
At the core of every heating system lies the heat source, which is the apparatus that transforms various forms of energy into the required thermal energy. This can be achieved through combustion of fuels, geothermal energy, or even waste heat recovery. Electromagnetic flow meters and pressure transmitters are used for trade settlement of energy measurement at the heat source:
· Electromagnetic Flow Meter: The Electromagnetic Flow Meter measures the volumetric flow rate of conductive fluids with unwavering accuracy. It operates using a magnetic field and is particularly adept at handling slurries and viscous liquids without any mechanical obstruction, making it a reliable guardian of flow measurement.
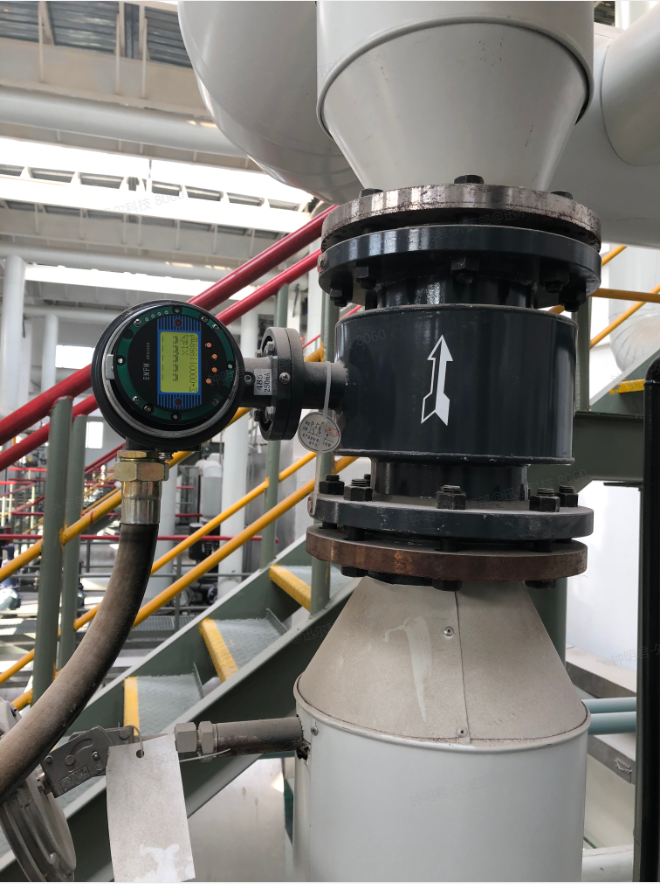

· Pressure Transmitter: The Pressure Transmitter measures the pressure of gases or liquids to ensure consistent pressure levels throughout the thermal system. It is essential for maintaining process control and safety, contributing to the overall stability and efficiency of thermal operations.
· Heat Network: The Veins of Distribution
The heat network, akin to the circulatory system of a city, is the pipeline system responsible for transporting and distributing the heating medium from the heat source to the heat users. It is divided into primary and secondary networks. The primary network carries the hot medium directly from the heat source, while the secondary network branches out to deliver the heat to individual consumers. This system ensures that heat is efficiently and safely delivered to where itsneeded.Liquid turbine flow meters and thermal flow sensors are used for process monitoring and control to optimize heat exchange efficiency.
· Ultrasonic Flow Meter: The Ultrasonic Flow Meter is the versatile scout, using sound waves to gauge the flow velocity of both liquids and gases. Its non-invasive nature allows it to thrive under a variety of conditions, including high pressure and temperature, making it an indispensable asset for precise flow monitoring across diverse thermal processes.
· Temperature Transmitter:The Temperature translates temperature readings into electrical signals that are crucial for maintaining optimal thermal conditions. It plays a pivotal role in boiler and heat exchanger operations, ensuring that temperatures are kept within safe and efficient parameters.
· Heat Exchange Station: The Nexus of Heat Transfer
Sitting at the crossroads of the primary and secondary networks is the heat exchange station, which serves as the heat transfer system. It extracts the high-temperature heat from the primary network and transfers it to the secondary networks hot water, which is then supplied to the end-users.Pipeline ultrasonic heat meters are used for trade settlement at the building level, ensuring fairness in heat distribution.
·Liquid Turbine Flow Meter: The Liquid Turbine Flow Meter measures the flow rate of liquids with precision by tracking the rotation of a turbine affected by fluid velocity. Known for its accuracy, it is widely valued for its contributions to systems that demand high-precision flow measurement.
·Thermal Flow Sensor: The Thermal Flow Sensor combines temperature and flow measurements to calculate the heat energy in a fluid. Its dual capabilities make it invaluable for heat tracing and energy management within thermal processes, providing a comprehensive understanding of energy dynamics.
·Heat Consumers: The Beneficiaries of Warmth
The heat consumers are the end-users of the heating system. They can be residential homes seeking comfort from the cold, commercial enterprises requiring a stable temperature for operations, or energy-intensive buildings that demand a consistent heat supply.
·Temperature Transmitter: Monitor fluid temperatures at the consumer end to ensure appropriate heat supply to users.
·Ultrasonic Flow Meters: Used for household metering to ensure the accuracy of trade settlements.
These instruments work in concert within the thermal control system, providing the necessary data for automated processes, optimizing energy use, and ensuring the safety and reliability of thermal operations. Each instrument, with its unique strengths, forms an integral part of the thermal power generation process.
Copyright © 2025 Tianjin Sure Instrument Co., Ltd. | All Rights Reserved 津ICP备08002549号-2
Hello, please leave your name and email here before chat online so that we won't miss your message and contact you smoothly.